Research Summary
Network (graph) is a powerful abstraction for representing interactions among entities in a system. The entities and their interactions are represented as nodes (vertices) and links (edges) of a network, respectively. Examples include various social networks, biological networks, the web graph, and collaboration networks of authors. Mining and analyzing networks and reasoning about them through modeling facilitate to understand and improve corresponding systems. Due to the advancement of computing and data technology, we are deluged with massive data from diverge areas such as business and finance, social media, biology, and other data driven disciplines. In the era of big data, the emerging network data is also very large. Social networks such as Facebook and Twitter have millions to billions of users. The World Wide Web has over a trillion web pages. Such massive networks motivates for efficient and scalable algorithms for mining and analysis. Research of Big Data and Scalable Computing lab, UNO strives to design such algorithms with applications to social, biological, and other technical systems.
Parallel Community Detection
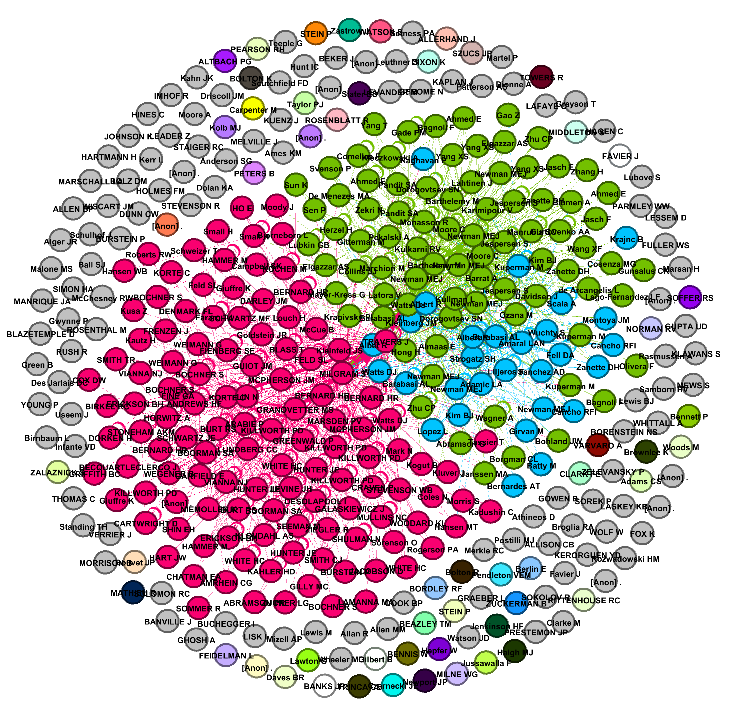
Complex systems are organized in clusters or communities, each having distinct role or function. In the corresponding network representation, each functional unit (community) appears as a tightly-knit set of nodes having a higher connection inside the set than outside. Finding communities may reveal the organization of complex systems and their function. We are currently working on designing parallel scalable algorithms for detecting communities in large-scale networks.